我是使用pymssql完成的sqlserver,首先下载符合版本的pymssql的whl,然后安装,在pycharm的default setting->project Interpreter中确定项目的Interpreter有pymssql,然后就开始了~
` # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import hashlib
import hmac
import json
import pymssql
from requests import Response
from rest_framework import status, generics
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from django.http import HttpResponse, HttpRequest
@api_view([\'GET\', \'POST\'])
def userlogin(req,format=None):
ms = MSSQL(host=\"你的IP地址\", user=\"你的数据库账号\", pwd=\"你的数据库密码\", db=\"你的数据库名\")
if req.method == \'GET\':
username = req.GET[\'username\']
password = req.GET[\'password\']
elif req.method == \'POST\':
username= req.POST[\'username\']
password = req.POST[\'password\']
newsql = \"select * from System_Users where Mobile = \'\"+username+\"\'\"
print(newsql)
reslist = ms.ExecQuery(newsql.encode(\'utf-8\'))
# //验证password加密后==LoginPwd
print(password)
print(reslist[0].get(\"LoginKey\"))
if Encrypt(password,reslist[0].get(\"LoginKey\"))==reslist[0].get(\"LoginKey\"):
reslist =json_success(reslist)
else:
reslist =json_error(reslist)
# meizis = System_Users.objects.all()
# serializer = MeiziSerializer(reslist, many=True)
# return Response(serializer.data)
return HttpResponse(json.dumps(reslist, default=lambda obj: obj.__dict__), content_type=\'application/json\')
# return reslist
def Encrypt(password=\"\",salt = \"\"):
clearBytes=[]
hasheByte=[]
# # encoding = unicode
# clearBytes= bytes(salt.lower().strip()+password.strip(),encoding=\'Unicode\')
# salt = crypt.mksalt(crypt.METHOD_SHA512)
# 然后再进行数据加密:
# hasheByte = crypt.crypt(\"helloworld\", salt)
# hasheByte =crypt.crypt(clearBytes, salt)
# password = hmac.new(key=clearBytes, msg=password)
# 待加密信息
str =salt.lower().strip()+password.strip()
# 创建md5对象
hl = hashlib.md5()
# Tips
# 此处必须声明encode
# 若写法为hl.update(str) 报错为: Unicode-objects must be encoded before hashing
print(\'MD5加密前为 :\' + str)
hl.update(str.encode(encoding=\'utf-16\'))
print(\'MD5加密后为 :\' + hl.hexdigest())
hl.update(str.encode(encoding=\'UTF-8\'))
print(\'MD5加密后为 :\' + hl.hexdigest())
hl.update(str.encode(encoding=\'GBK\'))
print(\'MD5加密后为 :\' + hl.hexdigest())
hl.update(str.encode(encoding=\'GB2312\'))
print(\'MD5加密后为 :\' + hl.hexdigest())
print(password)
return password
def json_success(data, code=200, foreign_penetrate=False, **kwargs):
data = {
\"status\": code,
\"msg\": \"成功\",
\"data\": data,
}
print(data)
return data
def json_error(error_string=\"失败\", code=500, **kwargs):
data = {
\"status\": code,
\"msg\": error_string,
\"data\": {}
}
data.update(kwargs)
return data
class MSSQL:
def __init__(self, host, user, pwd, db):
self.host = host
self.user = user
self.pwd = pwd
self.db = db
def __GetConnect(self):
if not self.db:
raise (NameError, \"没有设置数据库信息\")
self.conn = pymssql.connect(host=self.host, user=self.user, password=self.pwd, database=self.db, charset=\"GBK\")
cur = self.conn.cursor()
if not cur:
raise (NameError, \"连接数据库失败\")
else:
return cur
def ExecQuery(self, sql):
cur = self.__GetConnect()
cur.execute(sql)
resList = cur.fetchall()
col_names = [desc[0] for desc in cur.description]
result = []
for row in resList:
objDict = {}
# 把每一行的数据遍历出来放到Dict中
for index, value in enumerate(row):
index, col_names[index], value
objDict[col_names[index]] = value
result.append(objDict)
# 查询完毕后必须关闭连接
self.conn.close()
return result
def ExecNonQuery(self, sql):
cur = self.__GetConnect()
cur.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
self.conn.close()
然后设置好url就ok了,这是在Django框架下,fask框架下链接数据库模块依然可以使用
补充知识:使用pycharm连接数据库—Sqlalchemy
初识sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column,String,INTEGER
#1.创建引擎
eng = create_engine(\”mysql+pymysql://root:admin@localhost/homework?charset=utf8\”)
print(eng)
#2.创建基类
Base = declarative_base()
#3.创建类(模型)
class Student(Base):
__tablename__=\”student1\”#指定表格名称
id = Column(INTEGER,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True)
name = Column(String(32),nullable=False)#非空约束
email = Column(String(32),unique=True)#唯一约束
#4.创建表格
Base.metadata.create_all(eng)
#5删除表格
Base.metadata.drop_all(eng)
创建出来的student1表
使用Sqlalchemy四部曲:
1、使用create_engine()#连接数据库
2、Base = declarative_base()# 生成orm基类,用于创建classes
3、Base.metadata.create_all(engine) #关联engine使用metadata创建数据库表
4、使用 session = Session(engine) #创建一个会话,便于后面对数据库进行实际操作
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column,String,INTEGER
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
#1.创建引擎
eng = create_engine(\"mysql+pymysql://root:admin@localhost/homework?charset=utf8\")
#2.创建基类
Base = declarative_base()
#3.创建类(模型)
class Student(Base):
__tablename__ = \"student2\"
id = Column(INTEGER,primary_key=True,autoincrement=True)
name = Column(String(32), nullable=False) # 非空约束
email = Column(String(32), unique=True) # 唯一约束
#4.创建表格
Base.metadata.create_all(eng)
#5.创建session
Session = sessionmaker(bind=eng)
session = Session()#创建session对象,相当于pymysql中的conn
#增加记录
# student = Student(name=\'刘备\',email=\'120@qq.com\')#创建student的对象
# session.add(student)#添加记录
# #批量增加
# session.add_all(
# [
# Student(name=\'张飞\',email=\'110@qq.com\'),
# Student(name=\'悟空\',email=\'111@qq.com\'),
# Student(name=\'宫本\',email=\'112@qq.com\'),
# Student(name=\'赵云\',email=\'113@qq.com\'),
# ]
# )
#查询操作
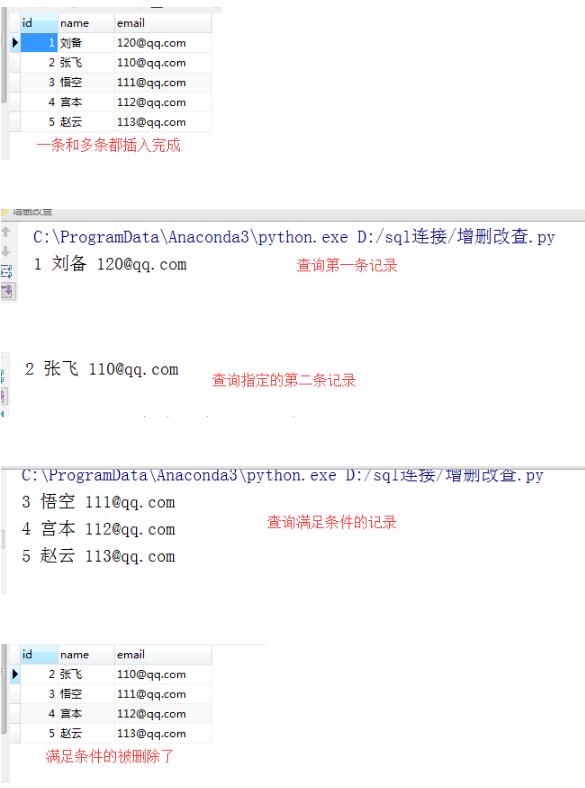
#first方法查询出第一条记录
# ret = session.query(Student).first()
# print(ret.id,ret.name,ret.email)
# #get方法查询指定记录
# student = session.query(Student).get(ident=2)#使用唯一标识ident不写也行查询第几条记录
# print(student.id,student.name,student.email)
#
# student = session.query(Student).filter(Student.id>2)#filter过滤相当于条件
# for stu in student:#这里的student是个对象,所以需要把他遍历出来显示查询出来的数据
# print(stu.id,stu.name,stu.email)
# #删除操作
# # student = session.query(Student).filter(Student.id<2).delete()
# # #方式一此方法可删除多个主要是因为filter,他是条件吗满足他的都可以被删除
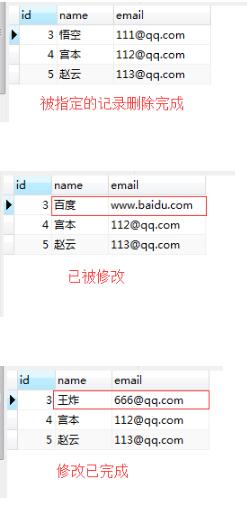
# student1 = session.query(Student).get(2)
# session.delete(student1)#方式二
# #修改操作
#单条修改
# student3 =session.query(Student).first()
# student3.name=\'百度\'
# student3.email=\'www.baidu.com\'
#指定条件修改
student4 =session.query(Student).filter(Student.id ==3).update({Student.name:\'王炸\',Student.email:\'666@qq.com\'})
session.commit()#提交事务
session.close()
以上这篇python 链接sqlserver 写接口实例就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持自学编程网。