1、python内置的sqlite3模块,创建数据库中的表,并向表中插入数据,从表中取出所有行,以及输出行的数量。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#创建SQLite3内存数据库,并创建带有四个属性的sales表
#sqlite3模块,提供了一个轻量级的基于磁盘的数据库,不需要独立的服务器进程
import sqlite3
#使用‘:memory:\'在内存中创建了一个数据库,创建了连接对象con来代表数据库
con = sqlite3.connect(\':memory:\')
#创建表名为sales的表,将这个字符串赋值给query
query = \"\"\"CREATE TABLE sales
(customer VARCHAR(20),
product VARCHAR(40),
amount FLOAT,
date DATE);\"\"\"
#使用连接对象的execute()方法执行query中的SQL命令
con.execute(query)
#使用连接对象的commit()方法将修改提交(保存)到数据库
con.commit()
#向表中插入几行数据
data = [(\'Richard Lucas\',\'Notepad\',2.50,\'2019-01-02\'),
(\'Jenny Kim\',\'Binder\',4.15,\'2019-01-05\'),
(\'Svetlana Crow\',\'Printer\',155.75,\'2019-02-03\'),
(\'Stephen Randolph\',\'Computer\',679.40,\'2019-02-20\')]
#将插入语句赋给变量statement,?是占位符
statement = \"INSERT INTO sales VALUES(?,?,?,?)\"
#因为有四个占位符,这里就需要提供一个包含4个值的元组,executemany()方法为data中的每个数据元组执行
#statement中的SQL命令,这里执行了四次insert命令
con.executemany(statement,data)
#将修改保存到数据库
con.commit()
#查询sales表,并将命令结果赋值给一个光标对象cursor,光标对象有execute、executemany、fetchone、
#fetchmany和fetchall方法
cursor = con.execute(\"SELECT * FROM sales\")
#返回结果集中的所有行
rows = cursor.fetchall()
print(rows)
print(\'………………\')
#查询结果中行的数量
row_counter = 0
for row in rows:
print(row)
row_counter += 1
print(\'………………\')
print(\'Number of rows: %d\' % (row_counter))
Spyder右下角打印出来的结果:
[(\'Richard Lucas\', \'Notepad\', 2.5, \'2019-01-02\'), (\'Jenny Kim\', \'Binder\', 4.15, \'2019-01-05\'), (\'Svetlana Crow\', \'Printer\', 155.75, \'2019-02-03\'), (\'Stephen Randolph\', \'Computer\', 679.4, \'2019-02-20\')] ……………… (\'Richard Lucas\', \'Notepad\', 2.5, \'2019-01-02\') (\'Jenny Kim\', \'Binder\', 4.15, \'2019-01-05\') (\'Svetlana Crow\', \'Printer\', 155.75, \'2019-02-03\') (\'Stephen Randolph\', \'Computer\', 679.4, \'2019-02-20\') ……………… Number of rows: 4
2、python内置的sqlite3模块,向表中插入新纪录
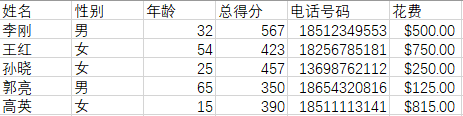
名称为“CSV测试数据.csv”的数据源:
将本地“CSV测试数据.csv”的数据导入到本地数据库football_game.db中:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#创建SQLite3内存数据库,并创建带有四个属性的sales表
#sqlite3模块,提供了一个轻量级的基于磁盘的数据库,不需要独立的服务器进程
import sqlite3
import csv
input_file = \"F://python入门//数据1//CSV测试数据.csv\"
#为一个简单的本地数据库football_game.db创建连接,football_game.db为数据库名称
con = sqlite3.connect(\'football_game.db\')
#创建了一个光标
c = con.cursor()
#如果表名存在,则删除它
drop_table = \"\"\"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS football_game;\"\"\"
c.execute(drop_table)
con.commit()
#创建表名为football_game的表,将这个字符串赋值给create_table
create_table = \"\"\"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS football_game
(name VARCHAR(20),
sex VARCHAR(10),
age INT,
score INT,
device_number VARCHAR(20),
cost VARCHAR(20));\"\"\"
#使用连接对象的execute()方法执行create_table中的SQL命令
c.execute(create_table)
#使用连接对象的commit()方法将修改提交(保存)到数据库
con.commit()
#从CSV格式的输入文件中读取要加载到数据库中的数据,创建file_reader对象,用于存储CSV中的数据集
file_reader = csv.reader(open(input_file,\'r\'),delimiter=\',\')
#从输入文件中读入第一行
header = next(file_reader,None)
#将输入的所有数据进行循环,先是每行循环,再是每列循环
for row in file_reader:
data = []
for column_index in range(len(header)):
data.append(row[column_index])
print(data)
c.execute(\"INSERT INTO football_game VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?)\",data)
#将修改保存到数据库
con.commit()
print(\'………………\')
#执行选择所有数据的SQL
output = c.execute(\"SELECT * FROM football_game\")
#返回结果集中的所有行,返回的是一个大的列表
rows = output.fetchall()
print(rows)
print(\'………………\')
for row in rows:
output = []
for column_index in range(len(row)):
output.append(str(row[column_index]))
print(output)
Spyder右下角打印出来的结果:
[\'李刚\', \'男\', \'32\', \'567\', \'18512349553\', \'$500.00 \'] [\'王红\', \'女\', \'54\', \'423\', \'18256785181\', \'$750.00 \'] [\'孙晓\', \'女\', \'25\', \'457\', \'13698762112\', \'$250.00 \'] [\'郭亮\', \'男\', \'65\', \'350\', \'18654320816\', \'$125.00 \'] [\'高英\', \'女\', \'15\', \'390\', \'18511113141\', \'$815.00 \'] ……………… [(\'李刚\', \'男\', 32, 567, \'18512349553\', \'$500.00 \'), (\'王红\', \'女\', 54, 423, \'18256785181\', \'$750.00 \'), (\'孙晓\', \'女\', 25, 457, \'13698762112\', \'$250.00 \'), (\'郭亮\', \'男\', 65, 350, \'18654320816\', \'$125.00 \'), (\'高英\', \'女\', 15, 390, \'18511113141\', \'$815.00 \')] ……………… [\'李刚\', \'男\', \'32\', \'567\', \'18512349553\', \'$500.00 \'] [\'王红\', \'女\', \'54\', \'423\', \'18256785181\', \'$750.00 \'] [\'孙晓\', \'女\', \'25\', \'457\', \'13698762112\', \'$250.00 \'] [\'郭亮\', \'男\', \'65\', \'350\', \'18654320816\', \'$125.00 \'] [\'高英\', \'女\', \'15\', \'390\', \'18511113141\', \'$815.00 \']
3、python内置的sqlite3模块,更新数据表中的记录
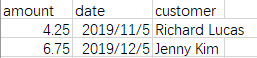
名称为“CSV测试数据.csv”的数据源:
更新表中的记录:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#创建SQLite3内存数据库,并创建带有四个属性的sales表
#sqlite3模块,提供了一个轻量级的基于磁盘的数据库,不需要独立的服务器进程
import sqlite3
import csv
input_file = \"F://python入门//数据1//CSV测试数据.csv\"
#使用‘:memory:\'在内存中创建了一个数据库,创建了连接对象con来代表数据库
con = sqlite3.connect(\':memory:\')
#创建表名为sales的表,将这个字符串赋值给query
query = \"\"\"CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sales
(customer VARCHAR(20),
product VARCHAR(40),
amount FLOAT,
date DATE);\"\"\"
#使用连接对象的execute()方法执行query中的SQL命令
con.execute(query)
#使用连接对象的commit()方法将修改提交(保存)到数据库
con.commit()
#向表中插入几行数据
data = [(\'Richard Lucas\',\'Notepad\',2.50,\'2019-01-02\'),
(\'Jenny Kim\',\'Binder\',4.15,\'2019-01-05\'),
(\'Svetlana Crow\',\'Printer\',155.75,\'2019-02-03\'),
(\'Stephen Randolph\',\'Computer\',679.40,\'2019-02-20\')]
#for tuple in data:
# print(tuple)
#将插入语句赋给变量statement,?是占位符
statement = \"INSERT INTO sales VALUES(?,?,?,?)\"
#因为有四个占位符,这里就需要提供一个包含4个值的元组,executemany()方法为data中的每个数据元组执行
#statement中的SQL命令,这里执行了四次insert命令
con.executemany(statement,data)
#将修改保存到数据库
con.commit()
#读取CSV文件并更新特定的行
file_reader = csv.reader(open(input_file,\'r\'),delimiter=\',\')
#从输入文件中读入第一行
header = next(file_reader,None)
#将输入的所有数据进行循环,先是每行循环,再是每列循环
for row in file_reader:
data = []
for column_index in range(len(header)):
data.append(row[column_index])
con.execute(\"UPDATE sales SET amount=?,date=? where customer=?;\",data)
#将修改保存到数据库
con.commit()
#查询sales表,并将命令结果赋值给一个光标对象cursor,光标对象有execute、executemany、fetchone、
#fetchmany和fetchall方法
cursor = con.execute(\"SELECT * FROM sales\")
#返回结果集中的所有行
rows = cursor.fetchall()
print(rows)
print(\'………………\')
for row in rows:
output = []
for column_index in range(len(row)):
output.append(str(row[column_index]))
print(output)
Spyder右下角打印出来的结果:
[(\'Richard Lucas\', \'Notepad\', 4.25, \'2019-11-05\'), (\'Jenny Kim\', \'Binder\', 6.75, \'2019-12-05\'), (\'Svetlana Crow\', \'Printer\', 155.75, \'2019-02-03\'), (\'Stephen Randolph\', \'Computer\', 679.4, \'2019-02-20\')] ……………… [\'Richard Lucas\', \'Notepad\', \'4.25\', \'2019-11-05\'] [\'Jenny Kim\', \'Binder\', \'6.75\', \'2019-12-05\'] [\'Svetlana Crow\', \'Printer\', \'155.75\', \'2019-02-03\'] [\'Stephen Randolph\', \'Computer\', \'679.4\', \'2019-02-20\']
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自学编程网。