一、前言
在程序中,有很多高效率的字符串处理方式,如果开发者能够完全掌握这些高效的字符串处理,往往在开发者也能事半功倍。比如针对于字符串的处理,也是自然语言处理的基础知识。
而python3中,处理字符串的库为:string。本篇将详细介绍各种字符串的高效处理方式。
二、首字母大写
对于英文单词组成的字符串来说,很多时候,我们需要对英文的首字母进行大写的变更。如果没有了解其高效率的函数,一般我们都通过循环,判断空格,取空格后一位的字母,判断其在ASCII中的编码后,取其大写替换掉该位置的字符串。
但是,python3中有一个函数可以直接将首字母大写,该函数为capwords()。下面,我们来通过一小段代码实现首字母大写的字符串变更。
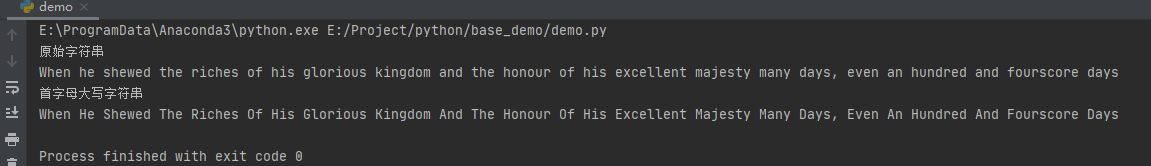
import string s = \"When he shewed the riches of his glorious kingdom and the honour of his excellent majesty many days, even an hundred and fourscore days\" print(\"原始字符串\") print(s) result = string.capwords(s) print(\"首字母大写字符串\") print(result)
运行之后,我们会得到全大写首字母字符串:
三、字符串模板
在string库中,字符串模板函数为string.Template(),它可以用来拼接字符串。示例代码如下:
import string
values = {
\"name\": \"liyuanjing\",
\"age\": \"13\",
}
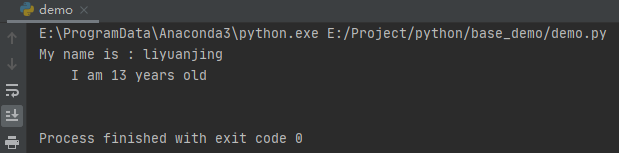
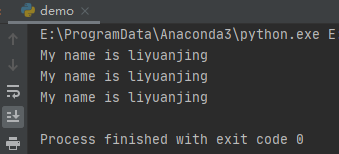
s = \"\"\"My name is : $name
I am $age years old
\"\"\"
template_str = string.Template(s)
print(template_str.substitute(values))
这里,我们使用字符串模板string.Template,然后通过函数substitute()进行字符串替换。
不过,这里有可能替换时values字典中没有对应的key怎么办?string库还给我们提供了一个函数safe_substitute()。
import string
values = {
\"name\": \"liyuanjing\",
\"age\": \"13\",
}
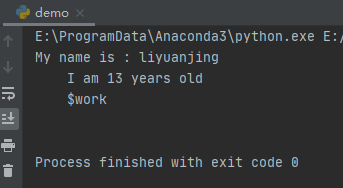
s = \"\"\"My name is : $name
I am $age years old
$work
\"\"\"
template_str = string.Template(s)
print(template_str.safe_substitute(values))
因为字典没有对应的值进行替换,所以会保留原始的字符串数据。效果如下:
四、高级模板
上面的模板使用方法是string库默认提供的规则体系。其实,我们还可以自定义模板的使用匹配方法,具体代码如下:
import string
class MyTemplate(string.Template):
delimiter = \'@\'
idpattern = \'[a-z]+_[0-9]+\'
values = {
\"name_1\": \"liyuanjing\",
\"age_1\": \"13\",
}
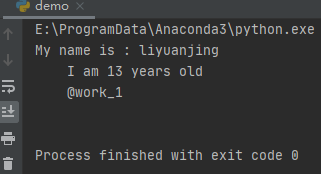
s = \"\"\"My name is : @name_1
I am @age_1 years old
@work_1
\"\"\"
template_str = MyTemplate(s)
print(template_str.safe_substitute(values))
这里,delimiter代表需要匹配的符号,默认符号\”$\”,博主替换成了‘@\’。其次,idpattern是values对应的key名字规则,这里用正则表达式规定,比如是\”字符串_数字\”。运行之后,效果如下:
五、format用法
基本用法
有过其他语言基础的都应该或多或少接触过format字符串替换。这里,我们直接来看看其基本的使用方式:
print(\"My name is {}\".format(\"liyuanjing\"))#大括号匹配,按顺序依次填充
print(\"My {1} is {0}\".format(\"liyuanjing\",\"name\"))#数字匹配,按位置依次填充
print(\"My {name} is {tom}\".format(tom=\"liyuanjing\",name=\"name\"))#关键字匹配,按关键字填充
运行之后,效果如下:
六、进阶用法
format函数不仅可以匹配替换字符串,还可以通过它对其文本,或者取小数某几位等等。下面,我们来看看这些用法如何实现。
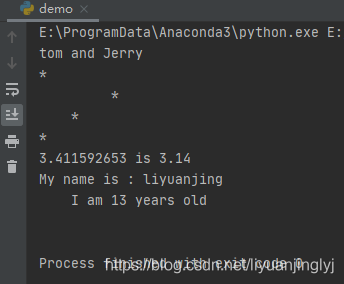
print(\'{} and {}\'.format(\'tom\', \'Jerry\'))
print(\'{:10s}\'.format(\'*\')) # 默认左对齐
print(\'{:>10s}\'.format(\'*\')) # 右对齐
print(\'{:^10s}\'.format(\'*\')) # 中间对齐
print(\'{:<10s}\'.format(\'*\')) # 左对齐
print(\'{} is {:.2f}\'.format(3.411592653, 3.1415926))#取2位小数
values = {
\"name_1\": \"liyuanjing\",
\"age_1\": \"13\",
}
s = \"\"\"My name is : {name_1}
I am {age_1} years old
\"\"\"
print(s.format(**values))
注释已经非常详细,这里不在赘述。效果如下:
七、高阶用法
format除了能做上面这些事情之外,还可以转换进制以及ASCII码符号等等。下面,我们来实现这些高阶用法。
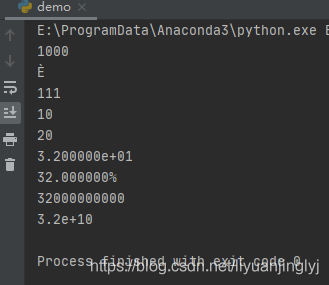
print(\'{:b}\'.format(8))#:b转换为二进制
print(\'{:c}\'.format(200))#:c转换Unicode字符串
print(\'{:d}\'.format(111))#:d转换十进制
print(\'{:o}\'.format(8))#:o转换八进制
print(\'{:x}\'.format(32))#:x转换十六进制
print(\'{:e}\'.format(32))#:e转换幂符号
print(\'{:%}\'.format(0.32))#:%转换百分值
print(\'{:n}\'.format(32000000000))#:n就是数值
print(\'{:g}\'.format(32000000000))#:n也是数值,不过特别大时转换为幂科学计数
运行之后,效果如下:
到此这篇关于Python的文本常量与字符串模板string库的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python string库内容请搜索自学编程网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自学编程网!