介绍
循环是计算机编程中最常用的结构之一。在Python中,有两种类型的循环:while循环和for循环。在本文中,我们将专注于while循环并提供20个实用示例,帮助您了解while循环的基本概念和用法。
Example 1: 简单的while循环
这是一个最简单的while循环,它只打印数字1到5:
i = 1
while i <= 5:
print(i)
i += 1
Example 2: 无限循环
这个例子展示了如何创建一个无限循环,需要使用break语句来退出循环:
while True:
x = input(\"输入 \'stop\' 来停止循环: \")
if x == \'stop\':
break
Example 3: 使用continue语句
continue语句用于跳过当前循环的剩余语句并继续下一次循环。在下面的示例中,我们跳过了所有奇数并打印了所有偶数:
i = 0
while i < 10:
i += 1
if i % 2 != 0:
continue
print(i)
Example 4: 循环中的else语句
在Python中,循环中的else语句与if语句中的else语句相似。它们在循环完成时执行。在下面的示例中,我们使用else语句在循环完成时打印一条消息:
i = 1
while i <= 5:
print(i)
i += 1
else:
print(\"循环已完成\")
Example 5: 使用while循环计算阶乘
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环计算输入数字的阶乘:
num = int(input(\"输入一个数字: \"))
factorial = 1
i = 1
while i <= num:
factorial *= i
i += 1
print(f\"{num} 的阶乘是 {factorial}\")
Example 6: 使用while循环计算斐波那契数列
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环计算斐波那契数列:
num = int(input(\"输入一个数字:\"))
a, b = 0, 1
while b < num:
print(b)
a, b = b, a + b
Example 7: 使用while循环查找列表中的元素
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环查找列表中的元素:
fruits = [\"苹果\", \"香蕉\", \"樱桃\", \"葡萄\"]
i = 0
while i < len(fruits):
print(fruits[i])
i += 1
Example 8: 使用while循环实现石头剪刀布游戏
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现石头剪刀布游戏:
import random
print(\"欢迎来到石头剪刀布游戏!\")
options = [\"石头\", \"剪刀\", \"布\"]
computer_choice = random.choice(options)
while True:
player_choice = input(\"请输入石头、剪刀或布:\")
if player_choice not in options:
print(\"输入无效,请重新输入。\")
continue
print(f\"电脑的选择是:{computer_choice}\")
if player_choice == computer_choice:
print(\"平局!\")
elif (player_choice == \"石头\" and computer_choice == \"剪刀\") or (player_choice == \"剪刀\" and computer_choice == \"布\") or (player_choice == \"布\" and computer_choice == \"石头\"):
print(\"你赢了!\")
else:
print(\"你输了!\")
break
Example 9: 使用while循环实现猜数字游戏
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现猜数字游戏:
import random
print(\"欢迎来到猜数字游戏!\")
number = random.randint(1, 20)
guesses = 0
while guesses < 6:
guess = int(input(\"请输入一个数字:\"))
guesses += 1
if guess < number:
print(\"你猜的数字太小了。\")
elif guess > number:
print(\"你猜的数字太大了。\")
else:
print(f\"恭喜你,你猜对了!你用了 {guesses} 次猜中了数字。\")
break
else:
print(f\"很遗憾,你没有猜中数字。数字是 {number}。\")
Example 10: 使用while循环实现加法练习
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现加法练习:
import random
print(\"欢迎来到加法练习!\")
correct_answers = 0
total_questions = 0
while True:
num1 = random.randint(1, 10)
num2 = random.randint(1, 10)
answer = int(input(f\"{num1} + {num2} = \"))
total_questions += 1
if answer == num1 + num2:
correct_answers += 1
print(\"回答正确!\")
else:
print(\"回答错误。\")
if input(\"是否继续?(y/n)\") == \"n\":
break
print(f\"你回答了 {total_questions} 道题目,其中 {correct_answers} 道题目回答正确。\")
Example 11: 使用while循环实现倒计时
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现倒计时:
import time
countdown = 10
while countdown > 0:
print(countdown)
time.sleep(1)
countdown -= 1
print(\"时间到!\")
Example 12: 使用while循环实现打印图案
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现打印图案:
i = 1
while i <= 5:
print(\"*\" * i)
i += 1
Example 13: 使用while循环实现计数器
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现计数器:
counter = 0
while True:
print(counter)
counter += 1
if counter == 10:
break
Example 14: 使用while循环实现密码验证
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现密码验证:
password = \"bazinga\"
while True:
attempt = input(\"请输入密码:\")
if attempt == password:
print(\"密码正确!\")
break
else:
print(\"密码错误,请重试。\")
Example 15: 使用while循环实现文件读取
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现文件读取:
with open(\"example.txt\") as f:
line = f.readline()
while line:
print(line.strip())
line = f.readline()
Example 16: 使用while循环实现文件写入
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现文件写入:
with open(\"example.txt\", \"w\") as f:
while True:
line = input(\"请输入一行文本:\")
if line == \"quit\":
break
f.write(line + \"\\\\n\")
Example 17: 使用while循环实现字符串反转
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现字符串反转:
text = \"Hello, World!\"
reversed_text = \"\"
i = len(text) - 1
while i >= 0:
reversed_text += text[i]
i -= 1
print(reversed_text)
Example 18: 使用while循环实现列表反转
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现列表反转:
fruits = [\"苹果\", \"香蕉\", \"樱桃\", \"葡萄\"]
reversed_fruits = []
i = len(fruits) - 1
while i >= 0:
reversed_fruits.append(fruits[i])
i -= 1
print(reversed_fruits)
Example 19: 使用while循环实现字符串切片
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现字符串切片:
text = \"Hello, World!\"
substring = \"\"
start = 7
end = 12
i = start
while i < end:
substring += text[i]
i += 1
print(substring)
Example 20: 使用while循环实现列表切片
在下面的示例中,我们使用while循环实现列表切片:
fruits = [\"苹果\", \"香蕉\", \"樱桃\", \"葡萄\"]
sliced_fruits = []
start = 1
end = 3
i = start
while i < end:
sliced_fruits.append(fruits[i])
i += 1
print(sliced_fruits)
在本文中,我们介绍了Python中的while循环及其用法,并提供了20个实用示例。这些示例可以帮助您更好地理解while循环的概念,并在实践中应用它们。
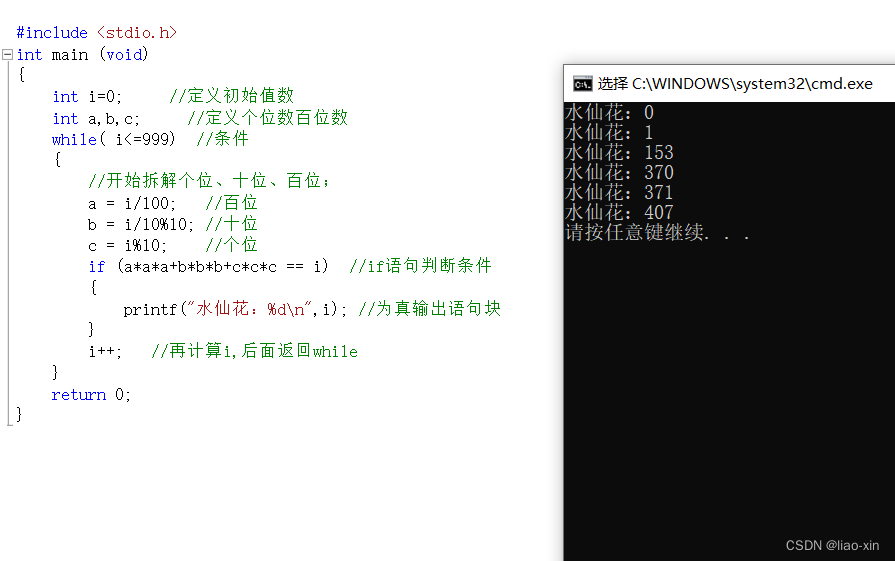
附:经典题目水仙花数
(从0至999之间各个位数的立方和等于本身的数等于水仙花数)代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main (void)
{
int i=0; //定义初始值数
int a,b,c; //定义个位数百位数
while( i<=999) //条件
{
//开始拆解个位、十位、百位;
a = i/100; //百位
b = i/10%10; //十位
c = i%10; //个位
if (a*a*a+b*b*b+c*c*c == i) //if语句判断条件
{
printf(\"水仙花:%d\\n\",i); //为真输出语句块
}
i++; //再计算i,后面返回while
}
return 0;
}
解释:
1、开始确定区间【0-999】
2、开始执行 i = 0;条件成立,执行语句块内容,拆解i的个位百位数,在用if语句判断是否成立,成立就输出i;
3、判断i的值,拆分个位十位百位;a = i/100; //百位; b = i/10%10; //十位;c = i%10; //个位
4、重复上面的操作,直到i=1000时,条件不成立,直接跳出while循环,运行while下面的语句。
结果:










暂无评论内容